VXLAN vs VLAN: Differences, Advantages & Disadvantages
Learn the core differences between VLAN and VXLAN
- Using the apt protocol for your cloud system is very crucial for optimal performance.
- Read this guide to understand why you should opt for VXLAN in certain situations over VLAN and vice versa.

Knowingly or unknowingly we make use of virtual servers, networks, desktops, storage, etc., in our daily lives to enjoy the convenience of cost-saving, enhanced features, and security.
In this guide, we will discuss VXLAN Vs VLAN networks, and understand which one is better than the other. Let us get right into the guide.
What is VLAN?
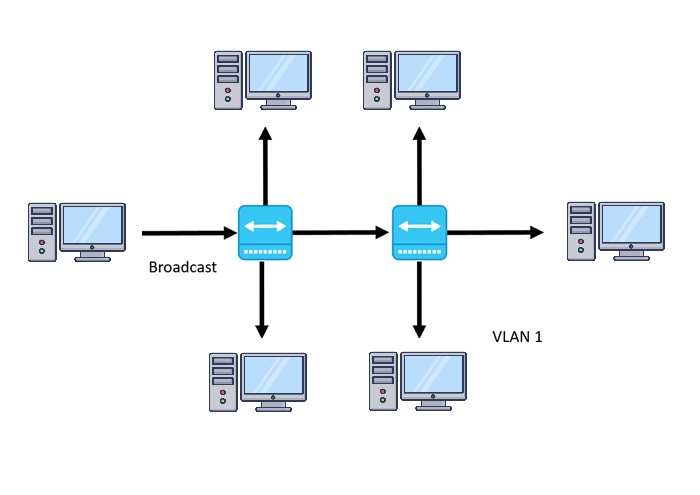
VLAN is an acronym for Virtual Local Area Network. As the name suggests, with VLAN you can create a virtual network in your local area for computers to connect and group together locally.
LAN can be used in an office, school, or building, which can come under a single network. VLAN is an extension of the Ethernet protocol with an extra header.
With that extra header, VLAN gains the ability to tag traffic with a number from 1 to 4094 (called VLAN ID). Each device connected in its respected VLAN ID will be securely separate and can be communicated over a firewall.
You can basically group multiple devices together using VLAN that frequently communicate with each other. For example, you can create a VLAN for the HR department, marketing team, and finance team, all of them having different VLAN IDs.
Some of the highlights of VLAN over LAN are that it is created by one or more LANs, its latency is less, it is cost-effective, the network packet is sent over to a specific broadcast domain, etc.
There are three types of VLAN or Virtual Local Area Network:
- Port-based VLAN – VLAN groups virtual local area networks by port, where a port can be configured manually to a member of VLAN.
- Protocol-based VLAN – This type of VLAN uses the traffic-based protocol to define filtering criteria for untagged packets.
- MAC-based VLAN – In this type of VLAN, the untagged packets are assigned virtual LAN allowing them to be classified based on their packet source address.
What is VXLAN?
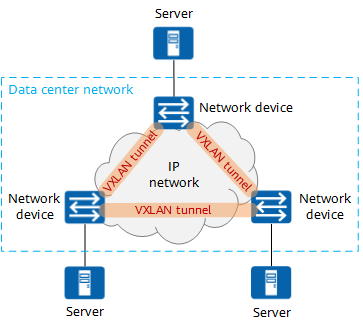
VXLAN stands for Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network and is an extension of the VLAN. VXLAN is a tunneling technique that establishes a logical tunnel on the IP network between the source and destination and forwards the user-side packets through the tunnel.
Expert tip:
SPONSORED
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to missing or corrupted system files and repositories of your Windows.
Be sure to use a dedicated tool, such as Fortect, which will scan and replace your broken files with their fresh versions from its repository.
It transmits layer 2 packets over Layer 3 network, which is ethernet over IP. VXLAN is used because of the limitation of VLAN where due to the 12-bit identifier you can only set up 4094 virtual networks.
Since VXLAN is a 24-bit identifier, you can set up around 16 million VXLAN IDs. The main purpose of VXLAN is to solve the issue of scalability.
Each physical server can set up multiple virtual servers with its own IP address and operating system. This lets you move a virtual machine from one physical server to another without affecting the user.
What are the differences between VLAN vs VXLAN?
| VLAN | VXLAN |
| VLAN is Virtual Local Area Network. | VXLAN is a Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network. |
| Scalable up to 4094 VLANs because of using a 12-bit identifier. | Scalable up to 16 million VXLANS because of using a 24-bit identifier. |
| Layer 2 ethernet connectivity to all the endpoints. | Layer 3 connectivity between each VXLAN tunnel endpoint. |
| Redundancy and loop avoidance are limited to ethernet-based solutions. | Redundancy and loop avoidance are limited to whatever is supported by Layer 2 or Layer 3. |
| It cannot be natively extended over a Layer 3 network segment. | VXLAN can be extended to whatever scalability the Layer 3 connectivity supports. |
| VLAN requires extra precaution and care and can be a bit frustrating to maintain in a large environment. | With the proper configuration adding and extending VXLANs is relatively easy, even in very large environments. |
| Simple to configure and maintain in small networks. | Manual configuration and maintenance are a bit challenging even in small networks. |
| It is less flexible in the multitenant environment. | More flexible as compared to VLAN in multitenant environments. |
| Makes use of the VLAN tag on the Layer 2 frame for encapsulation. | VXLAN uses MAC-in-UDP encapsulation to extend Layer2 segments across endpoints. |
| Since VLAN uses STP to block redundant paths, only half of the available paths are utilized. | VXLAN uses an underlying Layer 3 protocol to use all the available parts making it more cost-effective. |
What are the advantages and disadvantages of VXLAN and VLAN?
1. Advantages
1.1 VXLAN
- Increases scalability because of using 24-bit identifiers in the virtualized cloud environments allowing you to create 16 million isolated networks
- Runs over IP transport
- Negates the need for STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
- Gives you access to a large of endpoints
- Maintenance in a large environment is easy
- Uses Layer 3 protocol to utilize all available routing protocols
- Flexible and suitable for multitenant structure
1.2 VLAN
- It reduces the size of the broadcast domain
- VLAN is more cost-effective than LANs
- VLAN gets you an additional layer of security
- Easily manageable in small networks
- You can logically group devices based on their function rather than by their location
- VLAN lets you keep hosts separated
- You do not require additional hardware or cabling
2. Disadvantages
2.1 VXLAN
- Difficult to scale a centralized controller
- Manual configuration in small networks is a bit difficult
- Deployment of VXLAN is complicated
2.2 VLA
- A packet leak from one VLAN can transfer over to another
- Infection in one VLAN can carry over to another
- Requires an additional router to control large networks
- Cannot forward network traffic to other VLANs
Verdict: VLAN vs VXLAN
The main advantage of using VXLAN over VLAN is that it allows you to extend the overlay of the Layer 2 domain to the Layer 3 underlay network.
This basically eliminates the STP avoiding the redundant paths and utilizes all available paths. So, using VXLAN can help maximize the performance of the data center and reduce costs, especially in large environments.
You can deploy VXLAN via three methods:
- Host-based VXLAN – In this, the VXLAN runs on the host, where a virtual switch can act as a VTEP encapsulating and decapsulating the data packets.
- Gateway-based VXLAN – It is a hardware-based VXLAN, where the VTEP is within a switch or a router and is referred to as gateway VXLAN.
- Hybrid VXLAN – This is a combination of the above two VXLANs, where some VTEPs are on the host while some are on hardware. In this, the traffic flows from the source VTEP to the destination VTEP, which could be both hardware or software.
So, VXLAN has several benefits, one of the highlights being it allows you to change either network without the need to change the other network. Moreover, it lets you easily upgrade the virtual network by shifting the virtual machines to another server.
That is it from us in this guide. You should check out our guide that explains how you can easily resolve the problem where the VLAN ID is missing in Windows.
We also have a guide that lists some of the best network switches for a small business, that are powerful, efficient, and lets you control your business the way you want.
Feel free to let us know in the comments below if you were able to understand the differences between VLAN vs VXLAN by reading this guide or not.
Still experiencing issues?
SPONSORED
If the above suggestions have not solved your problem, your computer may experience more severe Windows troubles. We suggest choosing an all-in-one solution like Fortect to fix problems efficiently. After installation, just click the View&Fix button and then press Start Repair.