Your VPN is Blocked by The ISP? How to Unblock it
Switch your VPN to port 443 to bypass the blocking
- ISP blocking a VPN can prevent users from establishing a connection to a VPN server.
- The blockage can occur due to geolocation restrictions that block access from certain regions or IP ranges.
- You can unblock your VPN if it is blocked by ISP by switching your VPN connection to port 443.

Many users complained about ISP (Internet Service Provider) blocking their VPN (Virtual Private Network) connection. It means they are actively preventing users from connecting to a VPN server.
Hence, this article will discuss what to do if ISP blocks your VPN. Also, we have a detailed guide on using a VPN to access blocked sites on your device.
Why does my ISP block VPN?
- ISPs may block VPNs to mitigate potential security risks or ensure policy compliance.
- ISPs may block or throttle VPN traffic to manage their network resources.
- Sometimes, ISPs comply with geolocation regulations by blocking VPN connections.
- ISPs use network infrastructure or hardware incompatible with some VPN protocols.
- The ISP may have firewalls that actively block VPN traffic, thus preventing it entirely.
Users should note that these causes aren’t general and can vary on different computers depending on the circumstances. Nonetheless, we’ll take you through the detailed steps for unblocking your VPN.
You can check how to route all traffic through VPN on Windows 11.
What do I do if ISP blocks VPN?
Before proceeding with any advanced fixes, we recommend you go through the following preliminary checks:
- Try connecting to a different server location within your VPN client.
- If your ISP consistently blocks your current VPN, try a different VPN service and check if it helps.
- Enable any optional options like stealth mode or obfuscation in your VPN client.
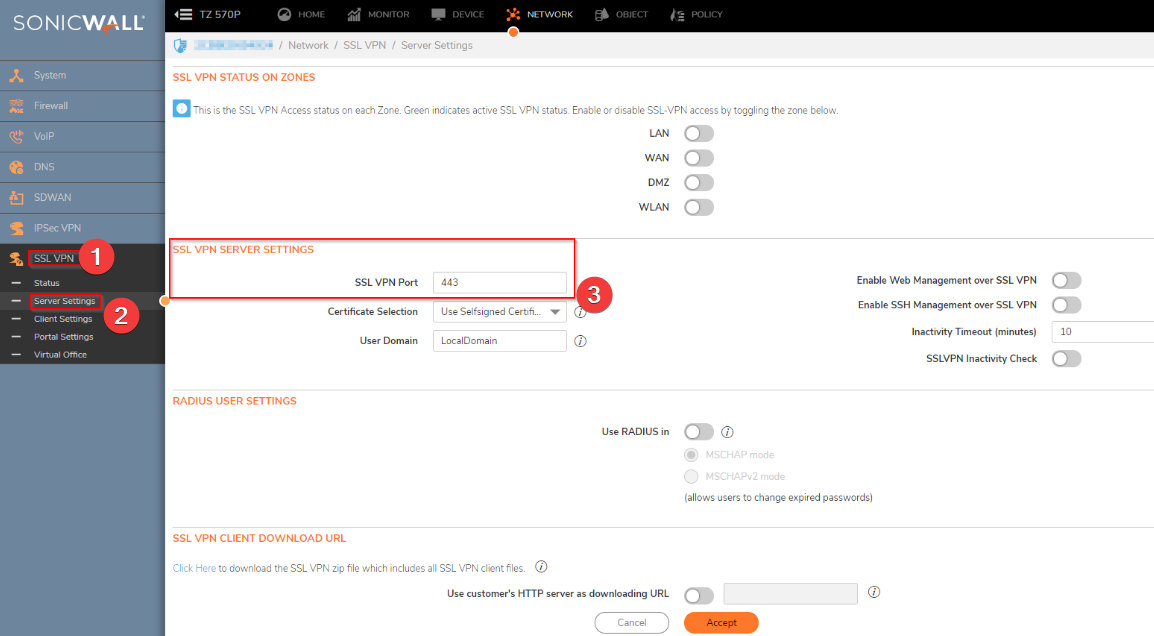
Switch your VPN connection to port 443
- Launch the VPN client application on your PC and navigate to the Settings or Preferences section.
- Find options for the VPN connection or Network settings in the settings menu.
- Locate the option to modify the default port used by the VPN. It might be labeled Port, Protocol, or Connection Type.
- Choose port 443 from the available list of ports or input it manually.
- If there is an option to specify a custom port, enter 443 in the appropriate field.
- Save the modified settings, and the VPN client will attempt to establish the VPN connection using port 443.
- Connect to the VPN and see if your internet traffic goes through the VPN and if you can access blocked content or services.
 NOTE
NOTE
Review your VPN provider’s documentation or contact their customer support to confirm if port 443 is available and supported.
In conclusion, we recommend you read through our article about how to change VPN IP addresses with or without the VPN in a few steps.
Likewise, you can check our guide on what to do if VPN stops working on your device.
Feel free to leave your suggestions and questions in the comments section below. We’ll like to hear from you.